The last Leap Day wasn’t just a curiosity of the Gregorian calendar. February 29, 2012, landed in the midst of a late-winter tornado outbreak stretching from Nebraska to east Tennessee.
The so-called Leap Day outbreak actually began the previous day with a pair of tornadoes north of North Platte, Nebraska.
They were weak – rated EF0 – damaging only an irrigation pivot, but they were historic; they were the first tornadoes ever observed and documented in the Cornhusker State during the month of February dating to 1950.
Another 42 tornadoes tore through parts of states from Kansas and Missouri to Kentucky and Tennessee on Feb. 28-29, 2012, claiming 15 lives and damaging or destroying hundreds of homes and businesses.
The first deadly tornado, rated EF2, spun up quickly over the city of Harveyville, Kansas, embedded in a line of severe thunderstorms.

Then, just after 1 a.m. CT on Leap Day 2012, an EF2 tornado tore a 22-mile long path through the heart of the entertainment district in Branson, Missouri.
Six theaters were damaged and 20 homes were destroyed. Fortunately, nobody was killed in the city popular for its live music venues. Branson’s hotels that are packed with thousands of tourists in the spring and summer were largely vacant.
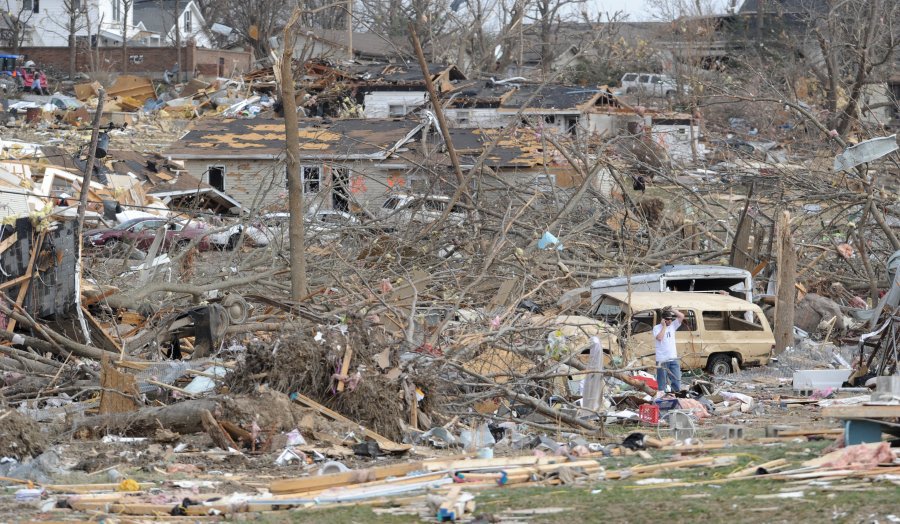
Just before sunrise, a southern Illinois town was ground zero for the outbreak’s most violent and deadliest tornado. Packing estimated winds up to 170 mph, an EF4 tornado tore through Harrisburg, Illinois, killing eight and damaging or destroying over 200 homes.
“The tornado came through the business district first, and it knocked a church down to its foundation,” said Lt. Tracy Felty of the Saline County Emergency Management Agency. “You kind of lose your bearings of where you’re at for a minute or two.”
Some houses were reduced to a pile of rubble where they once stood, while others were completely wiped off their foundation.
The tornado continued east-northeast, hitting the town of Ridgway, leaving St. Joseph’s Catholic Church in ruins.
Later that day, cancelled checks lofted by the tornado were found in Darmstadt, Indiana, some 70 miles from Harrisburg.
This was only the second February F/EF4 tornado of record in the state of Illinois and one of only five such intensity tornadoes in all of 2012.
Three other killer tornadoes struck Missouri on Leap Day, including an early-morning tornado in Stoddard County. A pair of late-afternoon tornadoes claimed three lives in Tennessee.
In the 15 prior Leap Days dating to 1950, there were tornadoes on only four of them, according to severe weather expert at The Weather Channel, Dr. Greg Forbes.
The 2012 outbreak featured the most tornadoes of any Leap Day. However, one other Leap Day was also deadly.
“February 29, 1952 had eight tornadoes, the strongest rated F4 with a total of five fatalities and 336 injuries,” said Forbes in an email. These tornadoes struck parts of the Tennessee Valley from middle Tennessee to north Georgia.
Forbes said with fewer weaker tornadoes reported in the mid-20th century than today, it’s possible the overall strength and impact of the Leap Day 1952 and 2012 outbreaks were comparable.